Modern and advanced Oocyte Donation treatment
Oocyte donation allows women with ovarian failure, poor oocyte health, or multiple failed IVF attempts to carry and deliver a pregnancy that carries the genetic contribution of the male partner.
THE LIFE PLUS HOSPITAL Care is COVID 19 Safe
1. Our Hospital premises are COVID safe
2. Regular sanitization of clinic & hospital premises
3. Immediate medical assistance through Online Consultation
Modern and advanced Oocyte Donation treatment
Oocyte donation allows women with ovarian failure, poor oocyte health, or multiple failed IVF attempts to carry and deliver a pregnancy that carries the genetic contribution of the male partner.
THE LIFE PLUS HOSPITAL Care is COVID 19 Safe
- Our Hospital premises are COVID safe
- Regular sanitization of clinic & hospital premises
- Immediate medical assistance through Online Consultation

Oocyte Donation
Oocyte donation allows women with ovarian failure, poor oocyte health, or multiple failed IVF attempts to carry and deliver a pregnancy that carries the genetic contribution of the male partner.
The phrase “third-party reproduction” refers to involving someone other than the individual or couple that plans to raise the child (intended parent[s]) in the process of reproduction. This includes using donated eggs, sperm, or embryos and gestational-carrier arrangements, in which the pregnancy is carried by someone other than the intended parent(s). Surrogacy, also sometimes referred to as a traditional gestational carrier, is a particular type of gestational-carrier arrangement where the woman who carries the pregnancy also provides the egg.
Let's Schedule Your Appointment
Treatment
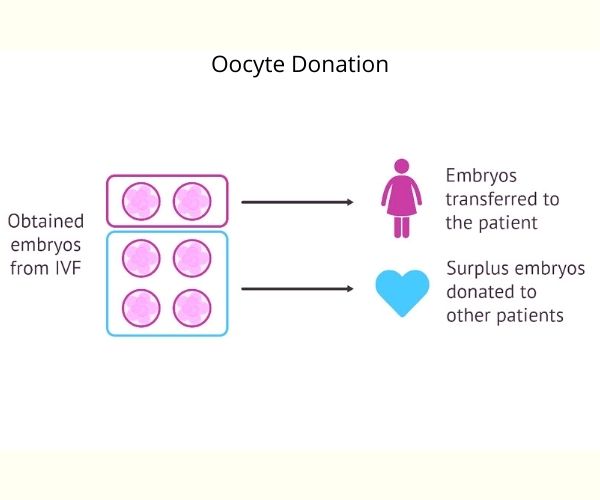
Indications for oocyte donation treatment
Oocyte donation was originally introduced for women with ovarian failure of various etiologies. Primary ovarian failure is often seen in women with X-chromosomal abnormalities or an FSH-receptor defect. Premature ovarian failure (POF) occurs in about 1% of women under 40 years of age and often no obvious cause can be found. Frequently, certain autoimmune conditions may occur at the same time. An increased risk of developing POF has been identified in fragile X premutation carriers. An important group of patients who benefit from oocyte donation is those who have had their ovaries removed because of endometriosis or neoplasia. Even in cases with a malign ovarian disease, e.g. epithelial carcinomas of stage IA and IB, dysgerminoma, teratoma, and granulosa cell tumors, conservative surgery with preservation of the uterus may be justified. In addition, oocyte donation offers a treatment option for women whose ovaries have been destroyed by chemotherapy or radiation therapy for malignancies, including Hodgkin’s disease or leukemia. An essential precondition for treatment of this patient group is, of course, that the disease is cured and that the uterus will respond adequately to hormone replacement therapy.

Our Doctors
Why The Life Plus Hospital?
 The Life Plus Hospital is COVID-19 safe
The Life Plus Hospital is COVID-19 safe
Your safety is taken care of by thermal screening, social distancing, sanitized clinics, and hospital rooms, sterilized surgical equipment, and mandatory PPE kits during surgery.
 Medical Expertise With Technology
Medical Expertise With Technology
Our Doctors spend a lot of time with you to diagnose your condition. You are assisted in all pre-assisted Hospitalisation process. We offer advanced laser and laparoscopic surgical treatment. Our procedures are USFDA approved.
 Assisted Surgery Experience
Assisted Surgery Experience
A dedicated Medical Coordinator assists you throughout the surgery journey from insurance paperwork, to free commute from home to hospital & back and admission-discharge process at the hospital.
 Post Natal Care
Post Natal Care
We offer free follow-up consultations and instructions including dietary tips as well as exercises to every patient to ensure they have a smooth recovery to their daily routines.
The Life Plus Hospital in Numbers
IVF / ICSI
Surrogacy
IUI
Healthy IVF Babies
GAMETE DONATION
Gametes are sperm or egg cells. Some aspects of sperm and egg donation are the same, others are specific to the type of gamete donated. In general, donors can be either known to the recipients or anonymous. There are different considerations for each type of donation (known versus anonymous), and those should be discussed with a mental-health professional (MHP) before treatment is started. For instance, with known donors, some of the suggested topics include how/when/if to tell the children/family/larger community, boundaries for involvement by the donor in the life of the child, and the feelings of the intended parent(s) about the biological connection (or lack thereof) to the child. With anonymous donors, suggested topics include how/when/if to tell the children/family/larger community, the possibility of a lack of important medical information in the future, and the feelings of the intended parent(s) about the lack of biological connection to the offspring
EGG DONATION
The first pregnancy resulting from egg donation was reported in 1984. Since then, egg donation has helped many struggling with infertility to conceive. With egg donation, the intended parents will have a genetic link to the child only if they contribute the sperm used to fertilize the egg. Egg donation requires in vitro fertilization (IVF), as the eggs are removed from one woman, fertilized in the laboratory, and the resulting embryo is transferred to the recipient’s uterus. The basic steps of egg donation with IVF are described below. For more information about IVF, please see the ASRM patient education booklet titled, Assisted Reproductive Technology.
- The first step is to find an egg donor. This can be either someone known to the intended parent(s) or an anonymous donor.
- The donor takes medication to stimulate her ovaries to produce multiple eggs and the eggs are collected. Sometimes, to share costs, the eggs from an egg-donation cycle are split among several recipients.
- Sperm from either the recipient’s male partner or a sperm donor are used to fertilize these eggs in the laboratory.
- An embryo (fertilized egg) is chosen and transferred to the uterus (womb) of the intended carrier and, hopefully, a pregnancy is established. The intended carrier can be the intended parent or another woman (gestational carrier), depending on the circumstances.
Reasons for Egg Donation
Egg donation is often used for women whose ovaries have either been surgically removed or are functioning poorly. Poor function can be due to premature menopause, severe diminished ovarian reserve, medical disorders, or exposure to toxins like chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Egg donation also is appropriate for women who were born without ovaries.
Other uses for egg donation have emerged in recent years. It is sometimes used to avoid passing down inherited diseases to a woman’s children. Egg donation also is used for women who have normal ovulation, but who have poor-quality eggs, for instance, women who have had multiple failed IVF cycles, women of advanced reproductive age (over age 38), and women with low response to medications for ovarian stimulation.
Who are Egg Donors?
There are several ways of obtaining donor eggs:
Anonymous donors: Women who are not known to the recipient(s). Donors may be found through egg donation programs or through agencies.
Known (directed donors): Women who are known to the recipient(s). The donor is generally a close relative or friend. In some instances, recipients advertise directly for donors in newspapers or on the internet. In these circumstances, the recipient(s) and the donor are known to each other in a limited way, and meet without an intermediary program or agency. Recipients should be cautious if recruiting donors directly without having an intermediary program or agency screen donors or without seeking legal counsel.
IVF programs: Women undergoing IVF may agree to donate their excess eggs to infertile patients. This source of donors is limited because this type of donation can be seen as coercive, particularly if the donors are offered a financial discount on their own IVF cycle.
Pregnancy Rates with Egg Donation
The pregnancy rate with egg donation depends on many factors but generally not on the age of the recipient. Success rates compiled by the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART) show that the average live-birth rate per egg-donation cycle was 46.2% overall (50.4% for fresh cycles and 38.4% for frozen cycles) across all egg donor programs. The major risk for egg donation is multiple gestations. Because many of the pregnancies miscarry before the number of fetuses can be counted, the percentage of multiple pregnancies actually may be higher. The current recommendation to reduce the risk of multiple gestations is to limit the number of embryos transferred. Most programs will limit the number of embryos transferred to one if the donor is between the ages of 21 and 37. Transfer of a single high-quality embryo, called elective single-embryo transfer (eSET), helps minimize the risk of multiple gestation.
SPERM DONATION
Insemination using donor sperm has been practiced for over a century, although the first published reports of such were in 1945. Since the late 1980s, with the emergence of HIV, donor insemination (DI) has been performed only with frozen and quarantined sperm to allow for time to test the donors. FDA and ASRM guidelines recommend that sperm be quarantined for at least six months before being used.
Reasons for Sperm Donation
Currently, DI is appropriate when the male partner has severe abnormalities in his semen and/or reproductive system, which may be present at birth (congenital) or develop later (acquired) and in other situations. For instance:
- Azoospermia (absence of sperm) can be due to a blockage (obstructive azoospermia), such as congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD) or previous vasectomy. Alternatively, azoospermia can be due to testicular failure (nonobstructive azoospermia) resulting from exposure to toxins like pesticides, radiation treatment, or chemotherapy.
- Severe oligozoospermia (decreased sperm count) or other significant sperm or seminal fluid abnormalities also are indications for DI.
- Ejaculatory dysfunction, such as inability to achieve or maintain an erection or to ejaculate, is a scenario where DI can be helpful.
- DI in place of an affected male’s sperm can help bypass significant genetic defects that can be passed to children.
- When there is no male partner, such as with single women who wish to become parents or lesbian couples who desire a pregnancy, but who lack a male partner, DI is needed for pregnancy.
Pregnancy Rates
Pregnancy rates with donor insemination depend on many factors, including the age of the female recipient and whether the recipient has other female fertility factors such as endometriosis, tubal disease, or ovulatory dysfunction. In general, the monthly chance of pregnancy ranges from 8% to 15%. A number of studies have shown that pregnancy rates using donor sperm with IUI are higher than with ICI when frozen semen is used. The risk of birth defects as a result of conceiving with donor insemination is no different than natural conception, and is in the range of 2% to 4%.
EMBRYO DONATION
Embryo donation is a procedure that enables embryos that were created by individuals undergoing fertility treatment to be transferred to other infertile patients to help them achieve a pregnancy. Reasons to have embryo donation include untreatable infertility that involves both partners, untreatable infertility in a single woman or woman without a male partner, recurrent pregnancy loss thought to be related to embryonic factors, and genetic disorders affecting one or both partners.
The process of embryo donation requires that the recipient(s) undergo(es) the appropriate medical and psychological screening recommended for all gamete-donor cycles. In addition, the female partner undergoes an evaluation of her uterine cavity and then her endometrium is prepared with estrogen and progesterone in anticipation of an embryo transfer.
Packages:
OD/ED Cycle (Single Cycle Plan): INR 2,00,000
Inclusions:
- Donor Charges
- Donor Medicines
- Donor Scans& Lab Tests
- Procedural Charges( Oocyte aspiration, Embryology, Embryo transfer)
- Media and Consumables
- Operation Theater charges
- Anesthetist Charges
- Nursing services charges
Exclusions:
- Recipient Medicines
- Recipient Scans And Lab tests
OD/ED Package: 2 Cycles Plan INR 5,00,000
In this package, If both Cycles fail the third cycle will be carried out free of procedural charges. Patients will have to bare only the medicine , scan and blood test charges.
Terms And Conditions:
This will be a non-refundable amount and will not be refunded at any stage of the treatment. And Frozen embryo transfer of supernumerary embryos from the previous cycle will also be considered as a cycle, however, patient can choose to undergo either a fresh cycle or a frozen embryo cycle but only one procedure is considered. There is a waiting period of 2 months in between the cycle
Donor Semen Charges: INR 1000/ sample
Get in Touch
Tell us about your problems and we’ll figure out the best treatment option for you.
Life Plus hospital
Women and Child Care Hospital in Indiranagar | LifePlus Hospital
At Life plus hospital, we offer a comprehensive range of women’s health services. The Department is managed by highly experienced lady gynecological doctors who offer specialized attention and compassionate care for women
Let's Schedule Your Appointment
IUI & IVF Success Story
https://youtu.be/3sBjEYtzV2Y
Oocyte Donation Faq's
We are always seeking healthy, non-smoking young women with normal menstrual cycles to join our Egg Donor Program. All potential donors must provide detailed information about you and your biological family members’ medical histories and educational backgrounds and complete a medical evaluation which includes a physical exam, pelvic ultrasound, and blood work. A consultation with our mental health counselor is also required.
Many couples are unable to conceive or carry a pregnancy using the female partner’s eggs. Some women may be without ovaries due to a medical condition, may have experienced premature ovarian failure or may not produce quality embryos. Some couples may also want to avoid passing on a serious genetic condition to their children.
Egg donation is commonly used by:
- Couples in which the woman is in menopause–who have poor quality or no eggs–but who want a biological child using her partner’s sperm
- Women with no ovaries but an intact uterus
- Women with genetic factors that they do not want to pass on to their children
- Same-sex male couples who plan to use gestational surrogacy
Oocytes (eggs) are retrieved from healthy young women, generally between 21 and 30 years old. Egg donors undergo screening as set forth by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), including a thorough medical history, physical exam, psychological screening and ovarian reserve testing to determine if she is likely to be a good donor candidate.